The phrase “Vascular Trauma” refers to an injury to a blood vessel - an artery, which conveys blood to an extreme or an organ, or a vein which returns blood to heart.
Vascular Surgeons classify these injuries by the sort of trauma that caused them.
Blunt injury can take place when a blood vessel is crushed or stretched.
A penetrating injury can happen when a blood vessel is punctured, torn, or severed.
Both types of vascular trauma can cause the blood vessels to clot(thrombosis) and interrupt blood flow to an organ or extremity, or cause bleeding which can lead to life-threatening hemorrhage.
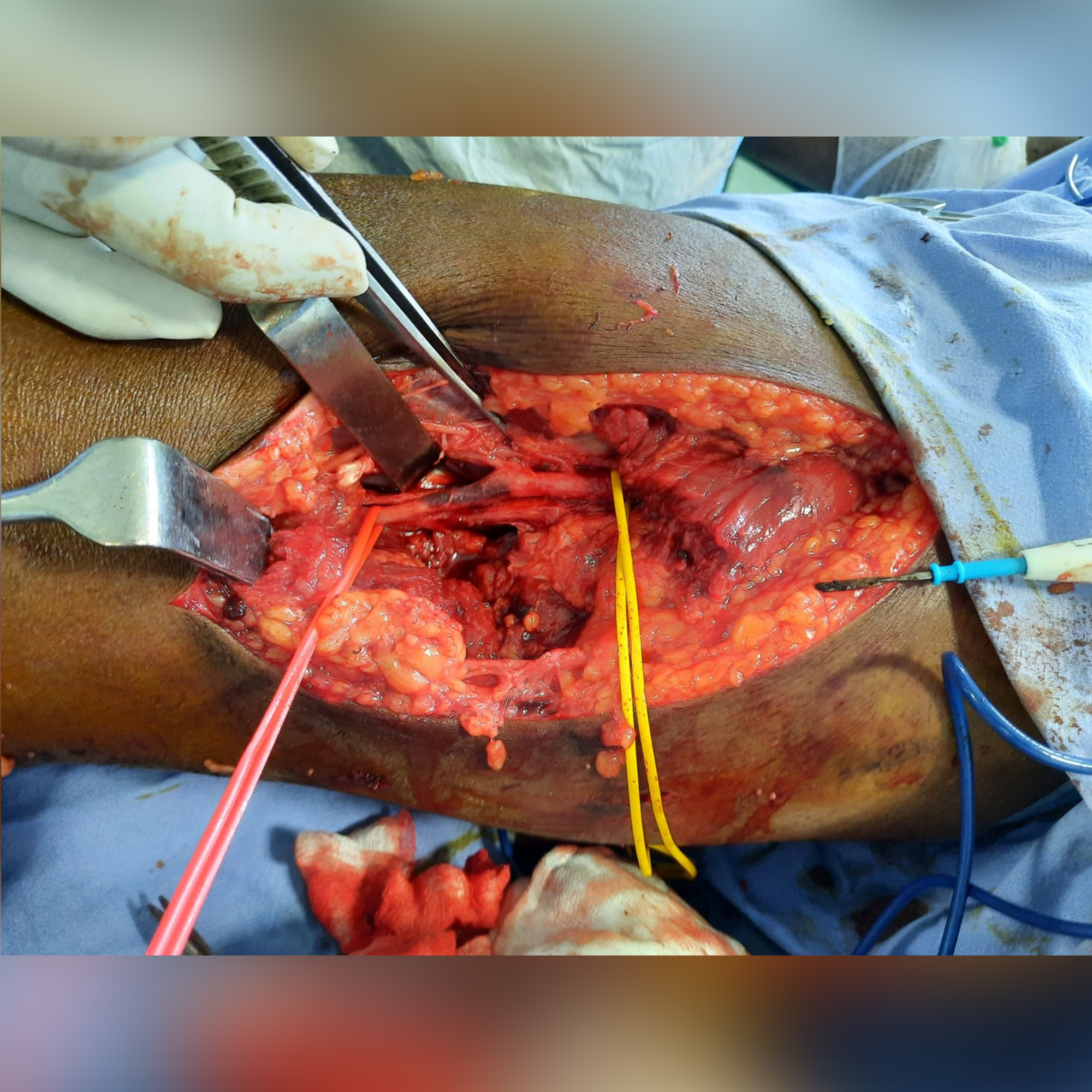
Surgical fixing of a blood vessel often requires a SURGICAL BYPASS
This procedure uses a prosthetic(synthetic graft) or a natural graft formed from a portion of a vein obtained from another location. If the injured vessel is a vein, may be repaired with a graft, sometimes the can supply can be tied off(ligated).
India is one of the fastest growing economies, with a fast rate of urbanization, industrialization, and motorization. Trauma has become the leading cause of death worldwide and addresses the leading cause of death among young adults in industrialized countries. Vascular injury of the extremities is an intricacy following both penetrating and blunt trauma. The incidence of these mechanisms varies widely according to the rate of trauma, in different regions across India. The general incidence of trauma and vascular wounds is increasing. Although vascular injuries are present in only 1%- 2% of injured patients, these patients account for a far greater share of morbidity, mortality, and resource utilization than those without such injuries. In recent studies, vascular injuries to the extremities account for 20%-50% of all vascular injuries. As is typical for the general population of injured patients, those with vascular injuries to the extremities tend to be young, with an average age in the 30s, and predominantly (70%-90%) male.
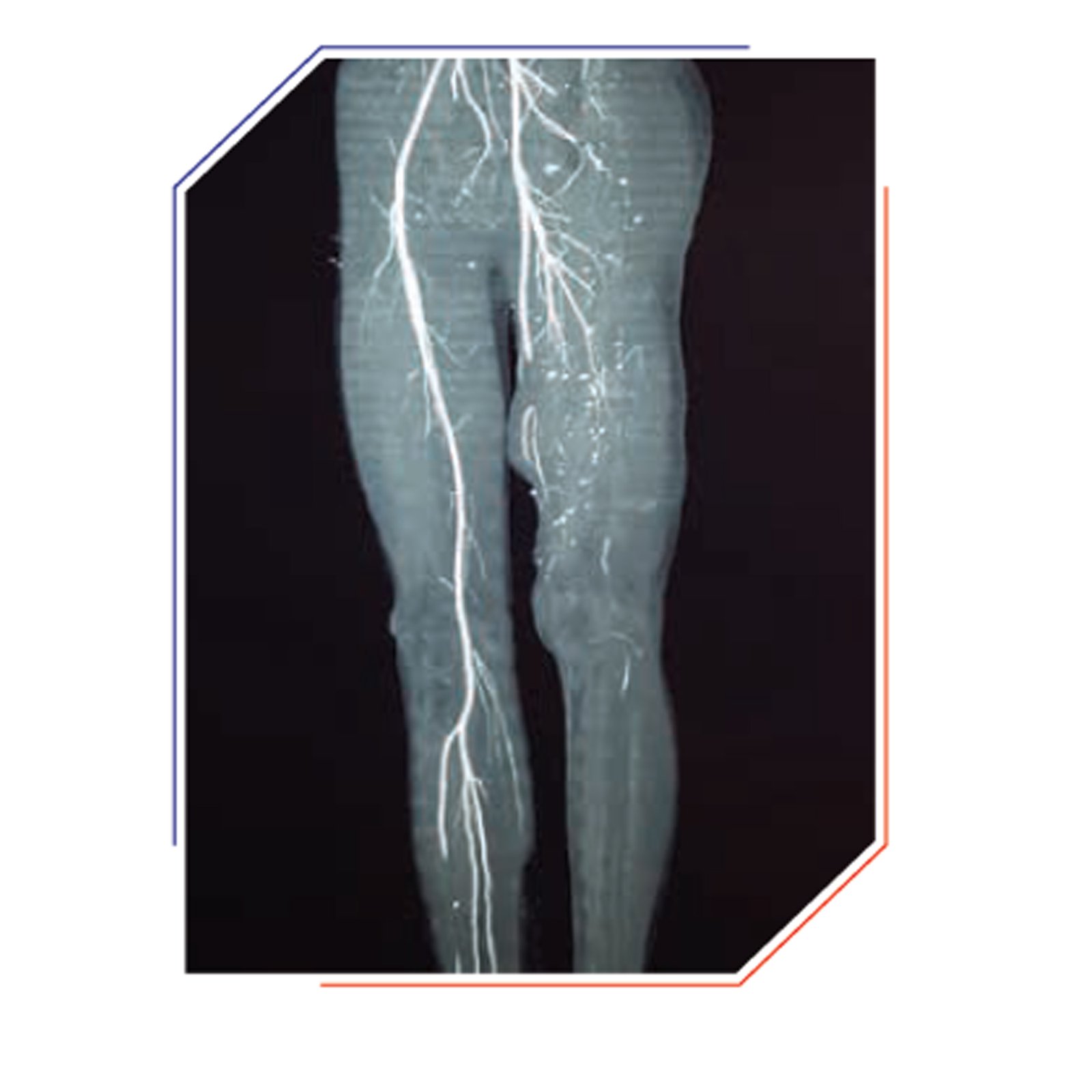
Consult a vascular surgeon for clinical assessment immediately. The doctor will perform a color Doppler test/computed tomography (CT) angiography of the injured limb and will explain to you the course of treatment. These imaging tests can detect vascular injury with good accuracy.
These can be broadly classified into four categories:
1. Emergency room management
In the emergency department, patients are managed as per Advanced Trauma Life Support (ATLS) guidelines. Life-threatening injuries are ruled out in the primary survey. During the primary survey, actively bleeding wounds are identified and hemorrhage is controlled. Patients may also require an urgent blood transfusion. When hemorrhage is under temporary control, the patient is transferred to the operating room or vascular cath lab for definitive vascular repair or ligation.
2. Open surgical treatment
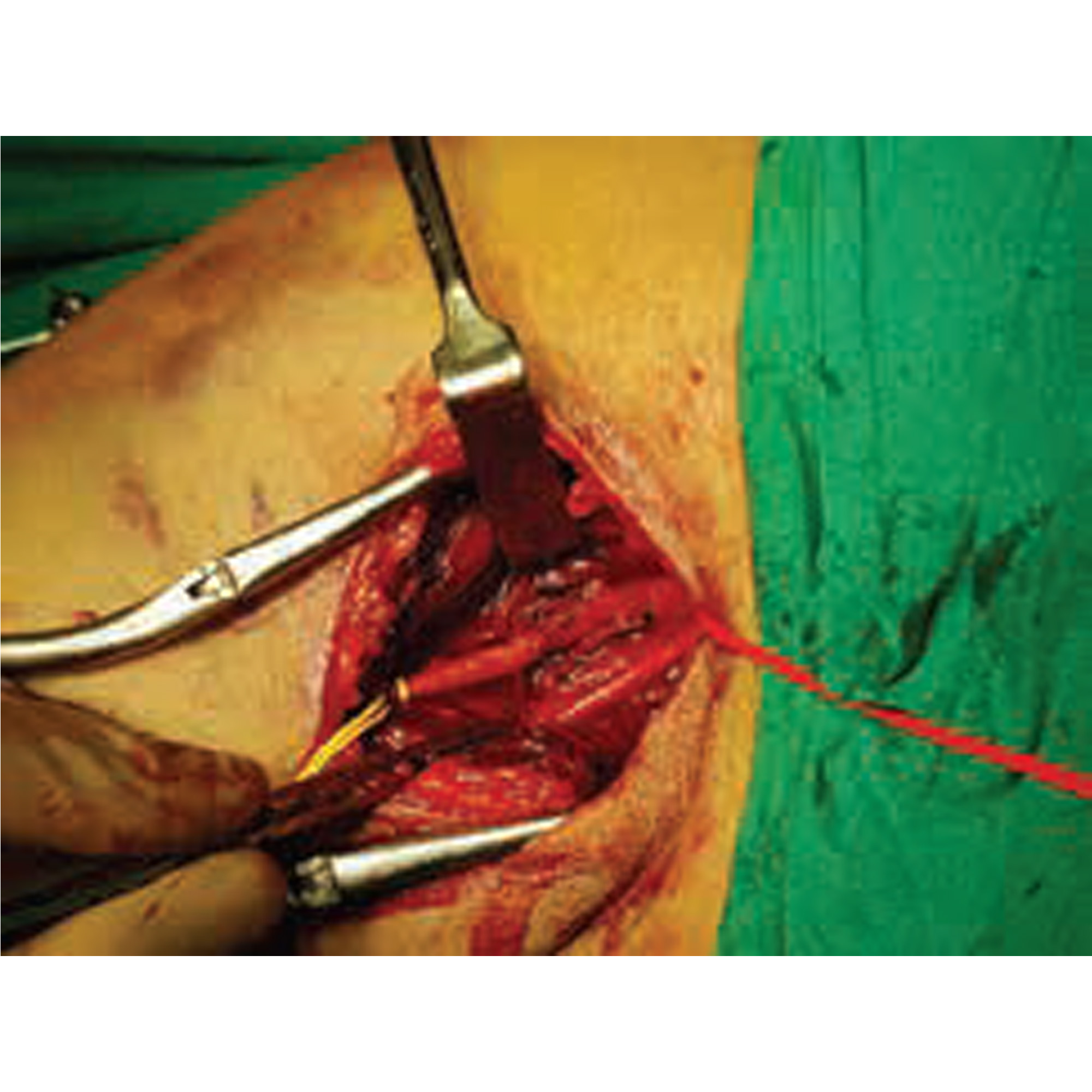
Open surgical control and bypass/primary repair remain the mainstays of the management of most vascular injuries to the extremities. It is a surgical procedure wherein two normal parts of blood vessels above and below the blocked area are connected by creating a bypass channel. Vascular repair is achieved with a reversed saphenous vein graft in most cases.
3. Endovascular treatment
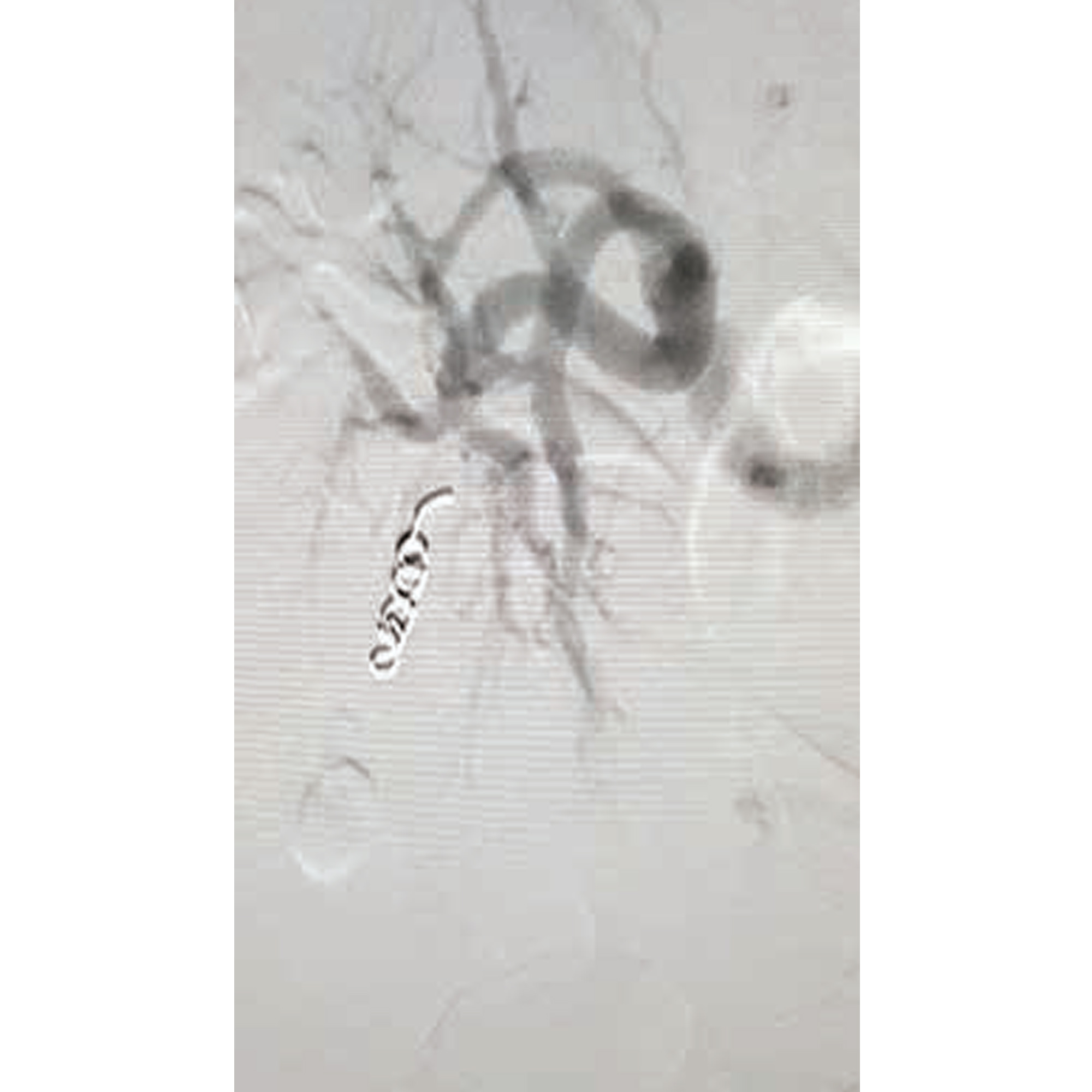
In a special scenario, the patient may have to be taken up to the vascular cath lab for emergency control of bleeding. This is particularly required when the injury is in a deeply situated vessel or the patient is unable to tolerate major surgery. A. Therapeutic Embolization: This procedure is used to block leakage from injured blood vessels. Different kinds of agents/particles/coils are used. Patients who will especially benefit from therapeutic embolization include those with multisystem injuries, ongoing bleeding, closed fractures, or late diagnosis of a traumatic aneurysm after orthopedic surgeries. B. Endovascular Stents and Stent Grafts: For the treatment of an intimal dissection or flap, endoluminal bypass can be performed using stents. In patients with traumatic aneurysms, a covered stent/stent graft can be used.