Carotid artery disease happens when fatty deposits (plaques) stop up the blood vessels that carry blood to your brain and head (carotid arteries).
Blockage in the carotid arteries in the neck is a common and significant reason for the development of brain stroke or paralysis, a potentially disabling and often life-warning condition. The role of a vascular specialist in eliminating this blockage is vital for the prevention of stroke. The causes or risk factors for blockage in the carotid artery are like those for blockages in the heart or leg artery.
Weakness or numbness on one side (leg, arm, or face), slurred speech, or visual disturbances are the usual presenting symptoms of a mini-stroke. Regardless of whether these events last for a few minutes or hours, they could be cautioning indications of carotid blockage and an impending stroke. These symptoms need to be evaluated by a carotid Doppler test, which is simple non-obtrusive sonography of the neck. A confirmatory angiography or CT angiography is performed if mediation is planned.
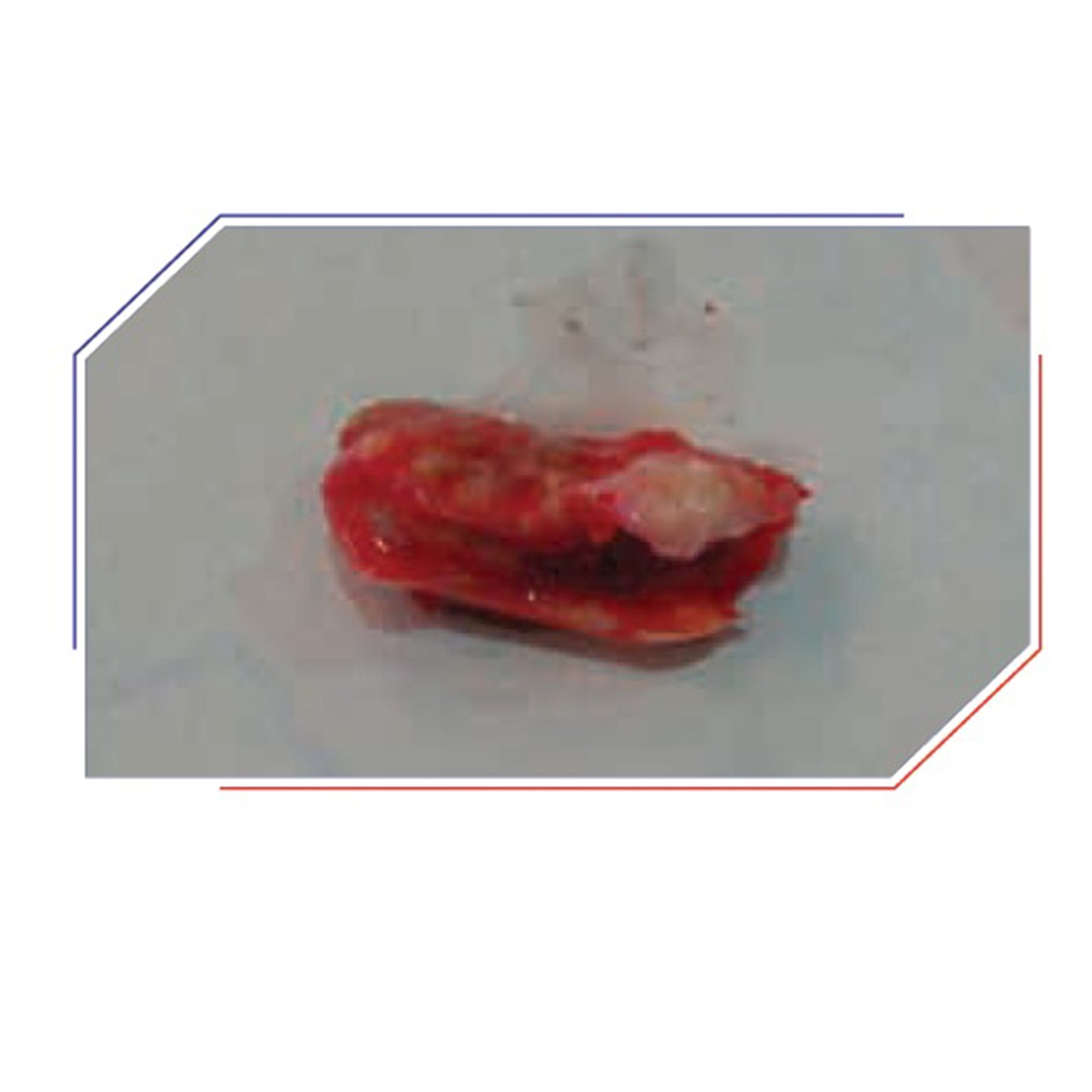
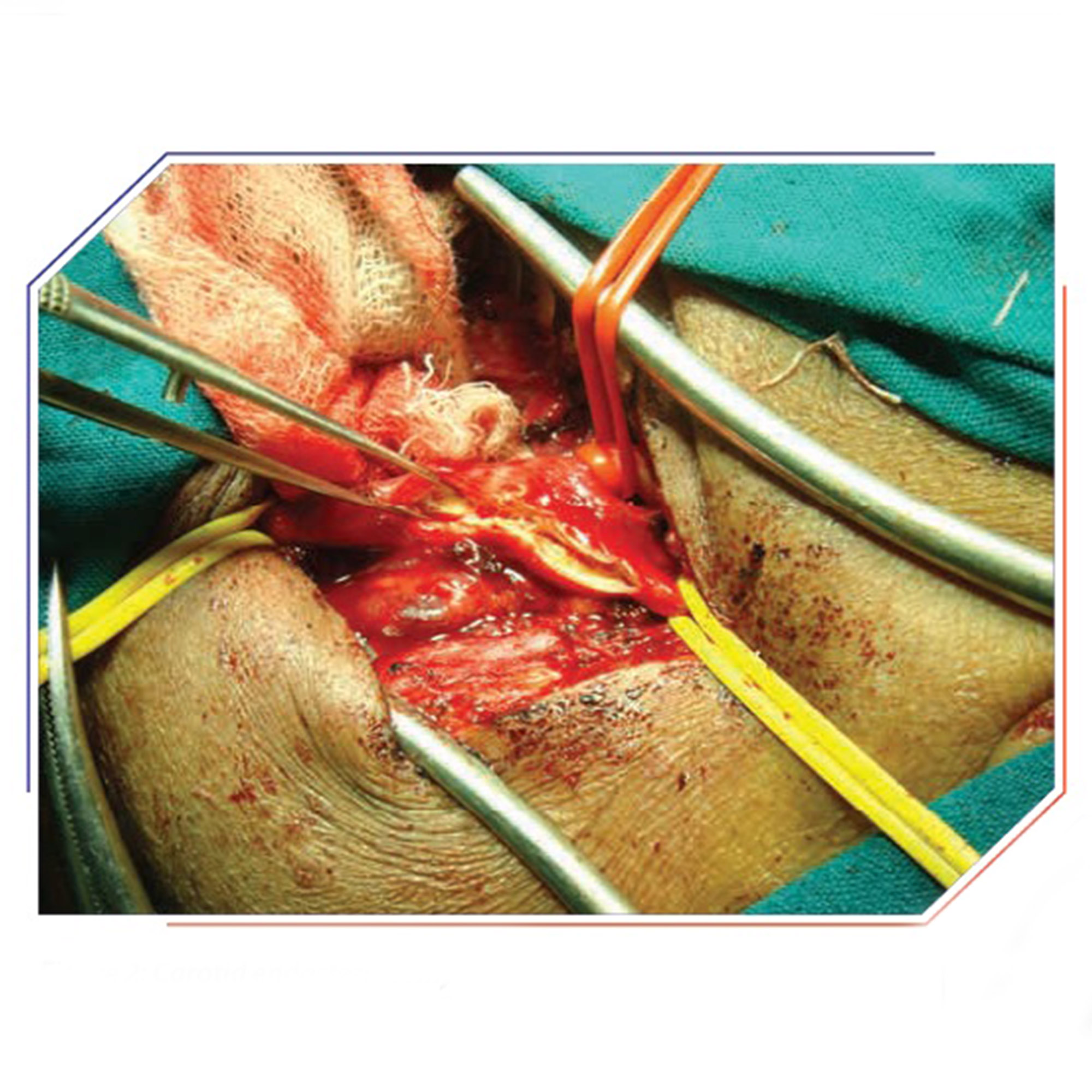
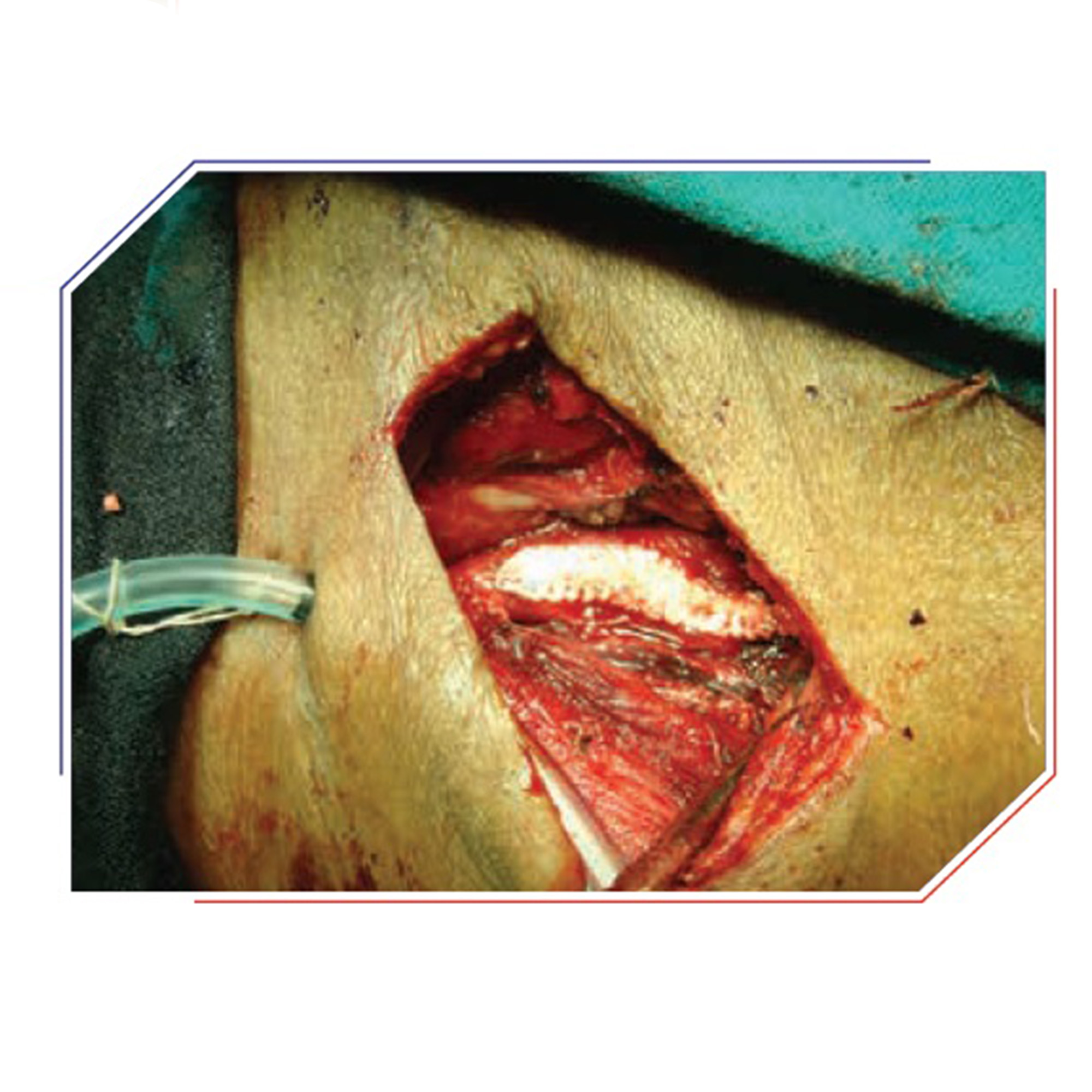
Minor blockages (less than 50%) are treated with blood thinners and cholesterol-controlling medicines. If the blockage is more than 50%, surgery or angioplasty with stenting is suggested. Carotid endarterectomy is an exceptional surgery for the removal of the carotid artery blockage. We routinely perform this procedure under loco-regional anesthesia for ease in intra-operative neurological monitoring. The artery is opened and the plaque carefully eliminated. During the surgery, a shunt is used to maintain blood flow to the brain. The artery is then fixed utilizing a vein or graft patch to prevent narrowing.
The other treatment option we offer is carotid angioplasty with stenting under a protection gadget. The protection gadget prevents small plaque particles from dislodging into the brain during stenting, subsequently reducing the complications of this method to less than 3%. It is fundamentally performed in high-risk patients or those with high carotid bifurcation.